Preview
Below you see the desktop video player we will build called, “Movie Monad.”
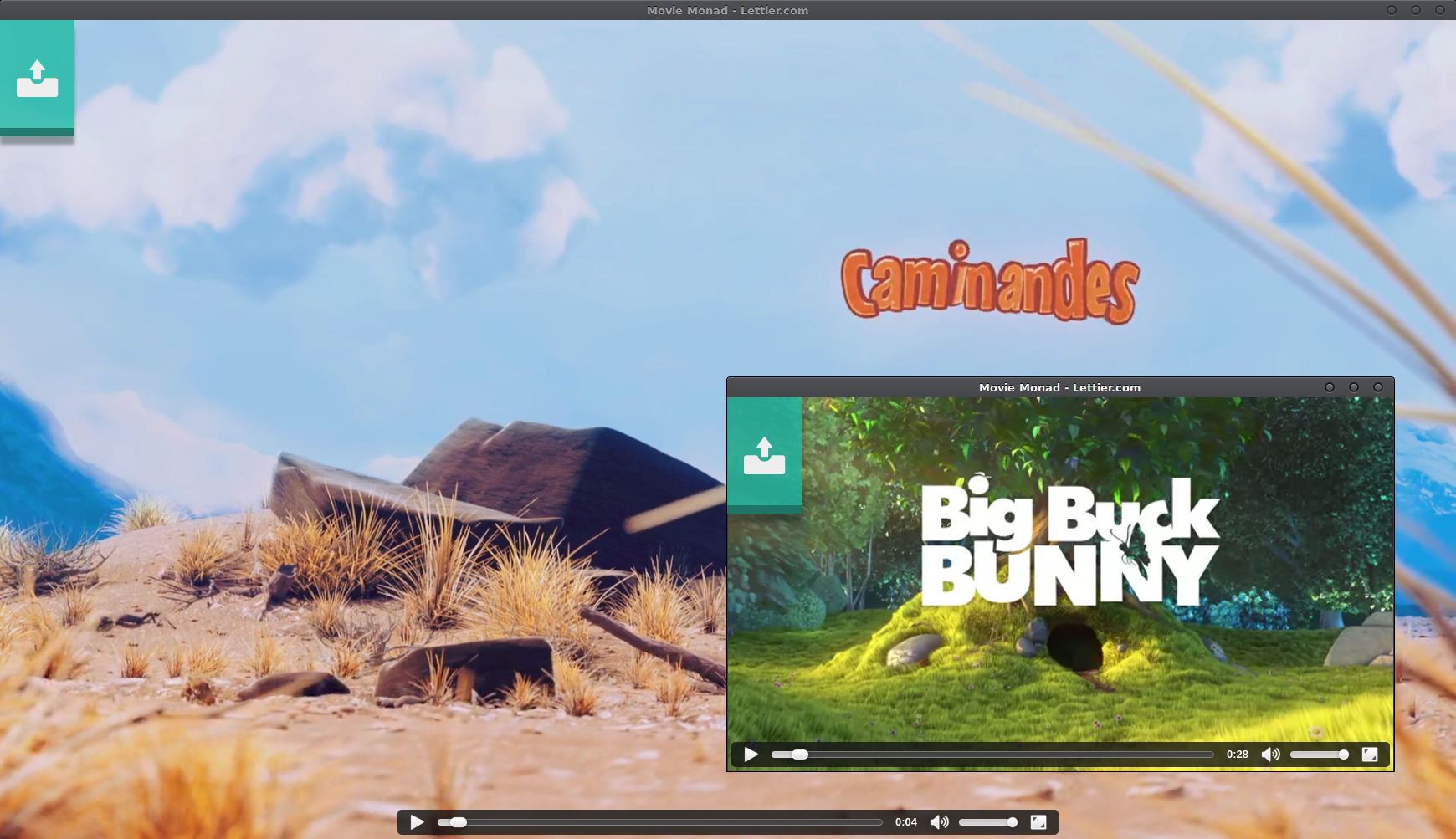
“Caminandes” and “Big Buck Bunny” from Blender Cloud.
Under the hood, the application uses the Electron framework which in turn uses Chromium and Node.js. Using only HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, you can use Electron to develop a desktop application. The nice part about Movie Monad, however, is that we will create the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript using Haskell.
Setup
In order to establish our build pipeline, we will need to setup our environment with a few tools, directories, and project files.
Stack
Stack will handle all of our Haskell environment needs from installing the compiler to managing our Haskell dependencies. The instructions contain all of the installation information you will need.
For a general Linux installation you could do:
cd Downloads
wget https://www.stackage.org/stack/linux-x86_64
tar xvzf stack-1.1.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
cd ~
echo 'export PATH="$HOME/Downloads/stack-1.1.2-linux-x86_64/:$PATH"' >> .bashrc
source .bashrc
# Or if you use ZSH.
echo 'export PATH="$HOME/Downloads/stack-1.1.2-linux-x86_64/:$PATH"' >> .zshrc
source .zshrc
stackProject Directory
With Stack installed, we will need to create our project directory.
cd ~
mkdir -p movieMonadWe will also need to define some additional directories for our project.
cd ~/movieMonad
mkdir -p src/html src/css src/js src/electronBoot branding conf dist binWith the directories in place, create the empty project files.
cd ~/movieMonad
touch src/html/Main.hs src/css/Main.hs src/js/Main.hs src/electronBoot/Main.hs conf/package.js branding/icon.png makefileYAML
To use Stack, you will need to define a stack.yaml file in the root of the directory.
cd ~/movieMonad
touch stack.yamlGo ahead and open this file with your favorite text editor and copy this information into the stack.yaml file.
resolver: lts-6.11
packages:
- '.'
extra-deps: []
flags: {}
extra-package-dbs: []Cabal
We will also need an movieMonad.cabal file which Stack will use to build our project. Make sure this file is located in the root of the project.
cd ~/movieMonad
touch movieMonad.cabalGo ahead and open this file with your favorite text editor and copy this information into the movieMonad.cabal file.
name: movieMonad
version: 0.1.0.0
synopsis: Desktop video player.
description: Please see README.md
homepage: https://github.com/lettier/moviemonad
license: Apache
license-file: LICENSE
author: David Lettier
copyright: 2016 David Lettier
category: Desktop
build-type: Simple
cabal-version: >=1.10
executable movieMonadCss
hs-source-dirs: src/css
main-is: Main.hs
default-language: Haskell2010
build-depends: base >= 4.7 && < 5
, clay
executable movieMonadHtml
hs-source-dirs: src/html
main-is: Main.hs
default-language: Haskell2010
build-depends: base >= 4.7 && < 5
, blaze-html
executable movieMonadJs
hs-source-dirs: src/js
main-is: Main.hs
default-language: Haskell2010
build-depends: base >= 4.7 && < 5
, cpphs
, fay
, fay-base
, fay-builder
, fay-dom
, fay-jquery
, fay-text
, fay-uri
, hlint
executable movieMonadElectronBoot
hs-source-dirs: src/electronBoot
main-is: Main.hs
default-language: Haskell2010
build-depends: base >= 4.7 && < 5
, cpphs
, fay
, fay-base
, fay-builder
, fay-dom
, fay-jquery
, fay-text
, fay-uriNVM
To install Electron we will need Node.js which we will get via NVM.
cd ~/Downloads
wget -qO- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/creationix/nvm/v0.31.2/install.sh | bash
cd ~/movieMonad
echo 'v4.0.0' > .nvmrc
nvm useElectron and Electron Packager
We will need Electron and Electron Packager to run and box up Movie Monad for distribution.
cd ~/movieMonad
nvm use
npm install -g electron electron-packagerPackage.json
Electron needs a package.json file to run. Copy the following into ~/movieMonad/conf/package.json.
{
"name" : "movieMonad",
"productName" : "movieMonad",
"author": {
"name": "David Lettier",
"url": "http://www.lettier.com/"
},
"version" : "0.0.0.1",
"main" : "boot.js"
}GNU Make
To automate our build process, we will use make. If you have ever used NPM scripts, you will be able to use make. Install make for your platform and then put the following in ~/movieMonad/makefile
# David Lettier (C) 2016
# http://www.lettier.com/
.RECIPEPREFIX != ps
PROJECT_NAME = movieMonad
HASKELL_PACKAGE_SANDBOX = ~/.stack/snapshots/x86_64-linux/lts-6.11/7.10.3/pkgdb/
FAY_PACKAGES = fay-jquery,fay-text
FAY_CC = HASKELL_PACKAGE_SANDBOX=$(HASKELL_PACKAGE_SANDBOX) fay --package $(FAY_PACKAGES) -p --Wall
all: build runElectron
build: clean gatherDependencies buildHaskell copyConf copyIcon buildElectronDists
clean: cleanDist cleanBin
cleanDist:
mkdir -p dist && mkdir -p dist_old && rm -rf dist_old && mv -f dist dist_old && mkdir -p dist
cleanBin:
mkdir -p bin && mkdir -p bin_old && rm -rf bin_old && mv -f bin bin_old && mkdir -p bin
gatherDependencies: installStackDependencies downloadJquery
installStackDependencies:
stack install --dependencies-only
downloadJquery:
wget http://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.10.2/jquery.min.js -O dist/jquery.js
buildHaskell: buildHtml buildCss buildJs
buildHtml:
stack ghc -- src/html/Main.hs -o bin/$(PROJECT_NAME)Html && bin/$(PROJECT_NAME)Html > dist/index.html
buildCss:
stack ghc -- src/css/Main.hs -o bin/$(PROJECT_NAME)Css && bin/$(PROJECT_NAME)Css > dist/all.css
buildJs:
$(FAY_CC) -o dist/all.js src/js/Main.hs && \
$(FAY_CC) -o dist/boot.js src/electronBoot/Main.hs
copyIcon:
cp branding/icon.png dist/
copyConf:
cp -R conf/. dist/
buildElectronDists:
mkdir -p dist/electronDists/ && electron-packager dist/ --all --version 0.37.2 --out dist/electronDists
runElectron:
electron dist/Project Directory Structure
With our build environment setup, our project directory should look like the following.
~/movieMonad
src/
html/
Main.hs
css/
Main.hs
js/
Main.hs
electronBoot/
Main.hs
conf/
package.json
branding/
icon.png
bin/
dist/
stack.yaml
movieMonad.cabal
makefileCode
The source code to Movie Monad consists of four major files.
HTML
Let us start with defining the HTML of Movie Monad. Since the application is fairly simple, we only need to define a little bit of structure.
{-# LANGUAGE OverloadedStrings #-}This language extension allows us to take a string literal such as "Some text." and use it for arguments that require type ByteString, Text, or String/[Char] (a ['l','i','s','t'] or array of characters).
import Text.Blaze.Html.Renderer.Pretty
import Text.Blaze.Html5 as H hiding (main)
import Text.Blaze.Html5.Attributes as AHere we import the needed Blaze modules. We will hide main as we will be defining it ourselves. When you see A–think Text.Blaze.Html5.Attributes.
main :: IO ()
main = putStrLn $ renderHtml $ docTypeHtml $ doWe start off with setting the document type, rendering the HTML to a string, and printing that string out.
H.head $ do
H.title "Movie Monad - Lettier.com"
styleSheet "https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Oswald"
styleSheet "https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/foundicons/3.0.0/foundation-icons.min.css"
styleSheet "all.css"
scriptSrc "jquery.js"
H.script $ toHtml' "if ('require' in window) { window.$ = window.jQuery = require('./jquery.js'); }"
scriptSrc "all.js"This is where we describe the <head><!-...-></head> section of our HTML document. We will be using a custom font from Google and icons from Foundation. The all.css and all.js files are our own custom CSS and JavaScript which we will define later. The jquery.js is a local copy of the jQuery JavaScript library. The JavaScript string requires the jQuery library and sets the jQuery object as a property of the window. If we run Movie Monad with Electron and without this line, an exception will be raised that jQuery is undefined. This little bit of JavaScript will be ignored if Movie Monad is loaded inside the browser–as a normal web page–instead of running it with Electron.
H.body $
H.div ! A.id "pageContainer" $ do
H.input ! A.id "fileInput" ! A.name "fileInput" ! A.type_ "file"
H.label ! A.for "fileInput" $ H.i ! A.class_ "fi-upload" ! A.title "Upload a Video File" $ empty
H.div ! A.id "videoContainer" $ empty
H.div ! A.id "statusMessage" $ emptyThe body of the document consists of a page container that holds a file input, label, video container, and a status message container which allows us to relay any feedback we have for the user.
This will translate into the following.
<body>
<div id="pageContainer">
<input id="fileInput" name="fileInput" type="file" />
<label for="fileInput">
<i class="fi-upload"></i>
</label>
<div id="videoContainer"></div>
<div id="statusMessage"></div>
</div>
</body>Notice how $ empty defines the inner HTML as blank for any defined tag.
toHtml' :: String -> Html
toHtml' = toHtml
empty :: Html
empty = toHtml' ""
styleSheet :: AttributeValue -> Html
styleSheet s = H.link ! A.href s ! A.rel "stylesheet" ! A.type_ "text/css"
scriptSrc :: AttributeValue -> Html
scriptSrc s = H.script ! A.src s ! A.type_ "text/javascript" $ emptyThese are helper functions to DRY up some of the code. Each one returns data with type Html. stylesheet "link" translates to <link href="link" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />.
Below is the entire ~/movieMonad/src/html/Main.hs file–be sure to copy it over.
{-
David Lettier (C) 2016
http://www.lettier.com/
-}
{-# LANGUAGE OverloadedStrings #-}
import Text.Blaze.Html.Renderer.Pretty
import Text.Blaze.Html5 as H hiding (main)
import Text.Blaze.Html5.Attributes as A
main :: IO ()
main = putStrLn $ renderHtml $ docTypeHtml $ do
H.head $ do
H.title "Movie Monad - Lettier.com"
styleSheet "https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Oswald"
styleSheet "https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/foundicons/3.0.0/foundation-icons.min.css"
styleSheet "all.css"
scriptSrc "jquery.js"
H.script $ toHtml' "if ('require' in window) { window.$ = window.jQuery = require('./jquery.js'); }"
scriptSrc "all.js"
H.body $
H.div ! A.id "pageContainer" $ do
H.input ! A.id "fileInput" ! A.name "fileInput" ! A.type_ "file"
H.label ! A.for "fileInput" $ H.i ! A.class_ "fi-upload" ! A.title "Upload a Video File" $ empty
H.div ! A.id "videoContainer" $ empty
H.div ! A.id "statusMessage" $ empty
toHtml' :: String -> Html
toHtml' = toHtml
empty :: Html
empty = toHtml' ""
styleSheet :: AttributeValue -> Html
styleSheet s = H.link ! A.href s ! A.rel "stylesheet" ! A.type_ "text/css"
scriptSrc :: AttributeValue -> Html
scriptSrc s = H.script ! A.src s ! A.type_ "text/javascript" $ emptyCSS
The CSS is fairly straightforward and nearly reads like a normal CSS file. Clay is a preprocessor like Sass or Less but you have the full expressiveness of Haskell at your disposal.
{-# LANGUAGE OverloadedStrings #-}
import Clay
import Clay.Box
import Clay.TransformLike before, we list our language extensions and necessary module imports.
main :: IO ()
main = putCss $ do
body ? do
backgroundColor "#323A45"
color "#eee"
fontFamily ["Oswald"] [sansSerif]
overflow hidden
height $ pct 100
width $ pct 100
marginAll $ px 0putCss will print out the generated CSS to standard out. You can see how we are defining the style for the main body of the document. Oswald is the custom font provided by Google. pct translates to %.
This block will translate roughly to the following.
body {
background-color: "#323A45";
/* ... */
} label ? do
borderBottomStyle solid
borderBottomColor $ rgba' 26 105 94 0.7969
backgroundColor $ rgba' 31 187 166 0.8
boxShadow (px 0) (px 10) (px 5) (rgba' 27 39 35 0.39)
fontSize $ px 60
paddingAll $ px 20
borderBottomWidth $ px 10
display inlineBlock
cursor pointerThis is the label for the file input box. It is here that we make it more like a button.
video ? do
height $ pct 100
width $ pct 100The video dimensions should always fill the window to make it responsive. The user can adjust the window size and the video will scale to match while at the same time keeping its aspect ratio.
"#pageContainer" ?
textAlign (alignSide sideLeft)
"#fileInput" ? do
width $ px 0
outlineWidth $ px 0
display none
"#videoContainer" ? do
position absolute
zIndex (-1)
top $ px 0
left $ px 0
height $ pct 100
width $ pct 100
"#statusMessage" ? do
position absolute
minHeight $ pct 100
minWidth $ pct 100
paddingTop $ pct 25
zIndex (-2)
top $ px 0
left $ px 0
width $ pct 100
height $ pct 100
fontSize $ px 60
textAlign $ alignSide sideCenterHere we use ID selectors to style the various containers, the file input, and the status message. The status message will always stay under the video.
paddingAll :: Size z -> Css
paddingAll s = padding s s s s
marginAll :: Size z -> Css
marginAll s = margin s s s s
rgba' :: Integer -> Integer -> Integer -> Double -> Color
rgba' r g b a = rgba r g b $ floor $ a * 255These functions provide more convenience over the functions provided by Clay. The padding and margin functions allow us to have uniform sizes without having to specify the same size for all four sides. Typically the alpha channel (in rgba) is expressed in decimal with a range of zero to one instead of an integer with a range of zero to 255.
Below is the entire ~/movieMonad/src/css/Main.hs file–be sure to copy it over.
{-
David Lettier (C) 2016
http://www.lettier.com/
-}
{-# LANGUAGE OverloadedStrings #-}
import Clay
import Clay.Box
import Clay.Transform
-- Color scheme: http://flatcolors.net/palette/757-carbon-flat-colorful
main :: IO ()
main = putCss $ do
body ? do
backgroundColor "#323A45"
color "#eee"
fontFamily ["Oswald"] [sansSerif]
overflow hidden
height $ pct 100
width $ pct 100
marginAll $ px 0
label ? do
borderBottomStyle solid
borderBottomColor $ rgba' 26 105 94 0.7969
backgroundColor $ rgba' 31 187 166 0.8
boxShadow (px 0) (px 10) (px 5) (rgba' 27 39 35 0.39)
fontSize $ px 60
paddingAll $ px 20
borderBottomWidth $ px 10
display inlineBlock
cursor pointer
video ? do
height $ pct 100
width $ pct 100
"#pageContainer" ?
textAlign (alignSide sideLeft)
"#fileInput" ? do
width $ px 0
outlineWidth $ px 0
display none
"#videoContainer" ? do
position absolute
zIndex (-1)
top $ px 0
left $ px 0
height $ pct 100
width $ pct 100
"#statusMessage" ? do
position absolute
minHeight $ pct 100
minWidth $ pct 100
paddingTop $ pct 25
zIndex (-2)
top $ px 0
left $ px 0
width $ pct 100
height $ pct 100
fontSize $ px 60
textAlign $ alignSide sideCenter
paddingAll :: Size z -> Css
paddingAll s = padding s s s s
marginAll :: Size z -> Css
marginAll s = margin s s s s
rgba' :: Integer -> Integer -> Integer -> Double -> Color
rgba' r g b a = rgba r g b $ floor $ a * 255JavaScript
Now we get to the more exciting part where we can produce JavaScript by writing Haskell. The library that provides this functionality is Fay.
Application Logic
The logic to Movie Monad is straightforward.
- The application waits for the user to click the label
- Once the user clicks the label, a file selection dialog opens up
- The user selects a file or cancels
- If the file is within the appropriate size range
- Read in the file data
- Take the file data and encode it into a data URL
- If the encoded data URL has the video MIME type
- Create a video element
- Set the source of the video element to the data URL
- Else
- Tell the user that the file is not a video
- Else
- Tell the user that the file is either too small or too large
- Clear out the video container
{-# LANGUAGE RebindableSyntax, OverloadedStrings, EmptyDataDecls #-}
import Prelude
import FFI
import JQuery
import Fay.TextWe’ve seen OverloadedStrings strings before but not RebindableSyntax nor EmptyDataDecls. RebindableSyntax allows us to redefine (rebind) operators defined in the Prelude. Note that Fay has its own Prelude. EmptyDataDecls allows us to declare data types without specifying what they are equivalent to (no constructors). We will use this to define some custom data types for objects returned from the JavaScript world.
data File
data FileReaderThese are our empty data type declarations. Notice that they do not have have constructors. File is a file object in the files property of the file input object. FileReader is the object we use to read in the video file selected by the user.
main :: Fay ()
main = startApp
startApp :: Fay ()
startApp = ready $ do
fileInput' <- fileInput
void $ change (const $ onFileInputChange fileInput') fileInput'Instead of the IO monad, we operate in the Fay monad returning the unit type. In other words, we perform some side effects and return nothing of interest (think void).
The start app function gets the file input object and setups a change event. When the file input changes, it will call the onFileInputChange callback.
The const function take two parameters but if you call it with only one, it returns a function that takes any parameter and returns the result of the first parameter you originally called const with. This is useful because change expects a function that takes an event and returns the unit type. However, onFileInputChange does not take an event. change will call what const returns (passing it an event), the event passed will be ignored, and onFileInputChange will be called.
Prelude> static = const 1
Prelude> :t static
static :: Num a => b -> a
Prelude> static "2"
1
Prelude> static 1255.5
1
Prelude> static []
1fileInput :: Fay JQuery
fileInput = select "#fileInput"Using Fay-jQuery, we select the element with the #fileInput ID.
newFileReader :: Fay FileReader
newFileReader = ffi "new FileReader()"ffi is short for foreign function interface. ffi allows us to call JavaScript from within our Haskell code. Notice how we return the FileReader data type (wrapped) within the Fay monad.
fileInputFiles :: JQuery -> Fay (Nullable [File])
fileInputFiles = ffi "%1['prop']('files')"The syntax here is a little cryptic but it translates to $('#fileInput').prop('files'); in JavaScript. The %1 syntax is the first argument JQuery in the type signature where JQuery is some object returned by the select function. Our return type is Nullable [File] which means that we may either get back Null or a list of files [File]. The Null type translates to null in JavaScript.
fileSize :: File -> Fay Int
fileSize = ffi "%1['size']"This takes a file object and calls size on it which returns an integer.
nullableFileSize :: Nullable File -> Fay Int
nullableFileSize nullableFile = case nullableFile of
Nullable file -> fileSize file
Null -> return 0This function helps with getting the size of a file that may actually be null. If the file is null, just return zero.
fileSizeLimit :: Int
fileSizeLimit = 51000000Because Movie Monad has to load the entire video file into memory, we have to limit the file size. If we do not limit the file size, the application could crash or freeze up for large video files. Ideally we would like to stream the video (play buffered chunks) from disk but the file reader API doesn’t allow for this. The file size limit number is in number of bytes–so the limit is roughly 48 megabytes.
fileInputFile :: JQuery -> Int -> Fay (Nullable File)
fileInputFile fileInput index = do
nullableFiles <- fileInputFiles fileInput
let files = case nullableFiles of
Nullable files -> files
Null -> []
if Prelude.null files || (Prelude.length files <= index)
then return Null
else return (Nullable $ files!!index)Taking the file input object, we gather up all of its input files. If there are no files, return null, otherwise return the requested file at the requested index.
fileReaderResult :: FileReader -> Fay Text
fileReaderResult = ffi "%1['result']"Once the file reader has brought the file into memory, we can access it via its result property.
addFileReaderEventListener :: FileReader -> Text -> (Event -> Fay ()) -> Fay ()
addFileReaderEventListener = ffi "%1['addEventListener'](%2, %3)"Taking a file reader object, specify a callback function to be called once the specified event type occurs.
// For example:
fileReader.addEventListener('load', function(event) {});setUpNewFileRead :: Nullable File -> Fay ()
setUpNewFileRead Null = return ()
setUpNewFileRead (Nullable file) = do
fr <- newFileReader
let onLoadCallback = const $ handleVideoFile fr
addFileReaderEventListener fr "load" onLoadCallback
readAsDataURL fr fileIf given a null file, do nothing. However, if we are given an actual file object, setup the callback and begin reading the file as a data URL.
onFileInputChange :: JQuery -> Fay ()
onFileInputChange fileInput = do
emptyVideoContainer
nullableFile <- fileInputFile fileInput 0
nfs <- nullableFileSize nullableFile
if (&&) (nfs > 0) (nfs <= fileSizeLimit)
then setUpNewFileRead nullableFile
else void $ setStatusMessage "File too small or large."This is the callback we used in startApp. The video container may contain a previously loaded video. We clear it out making way for the new video or a possible status message. If the file size is within the valid range, read the file, otherwise let the user know that the file size is not valid.
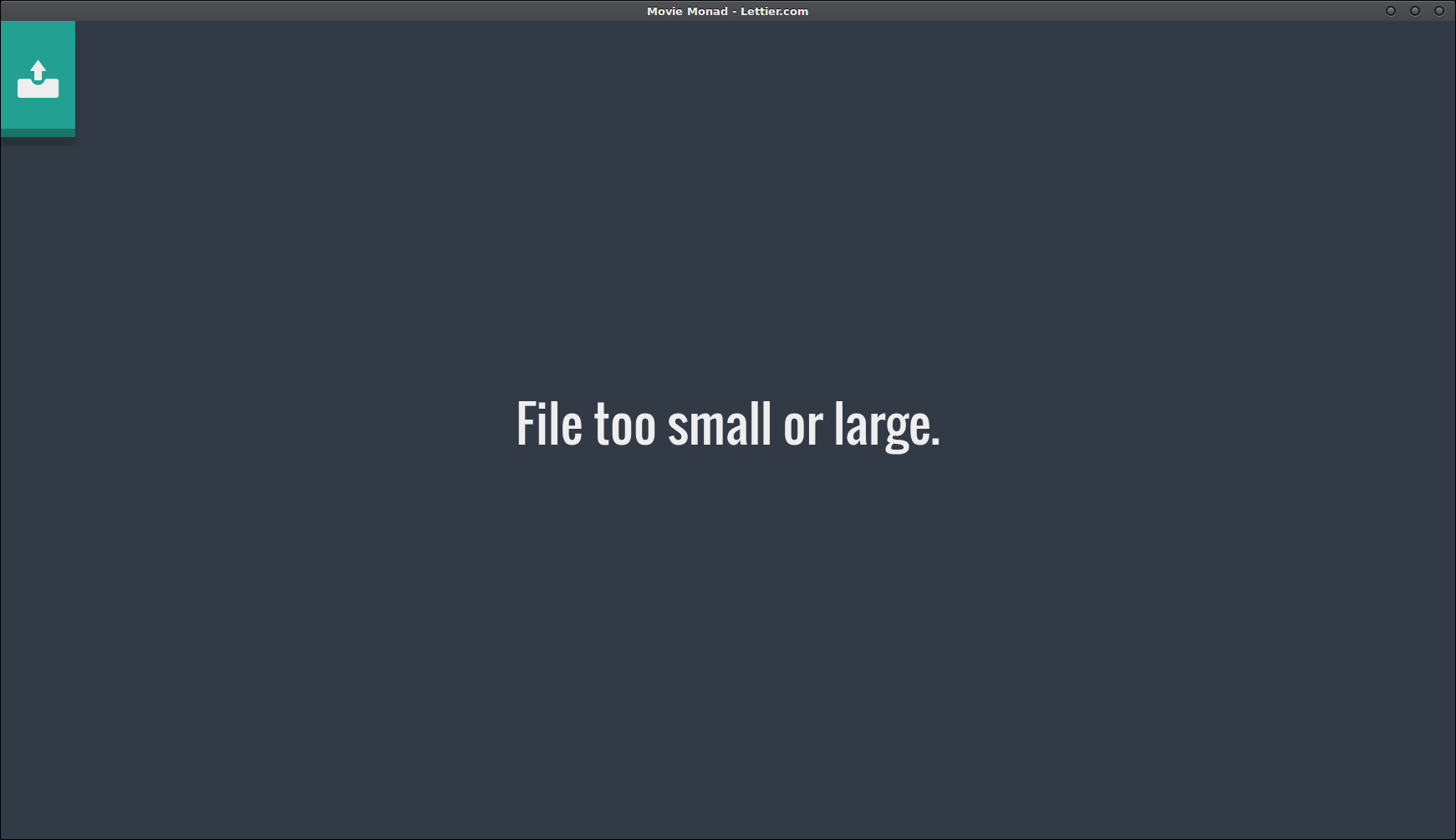
File is too small or large.
setStatusMessage :: Text -> Fay JQuery
setStatusMessage text = select "#statusMessage" >>= setHtml textSelect the status message element and set its inner HTML to the text passed.
videoContainer :: Fay JQuery
videoContainer = select "#videoContainer"Return the video container element.
addVideoElement :: Fay JQuery
addVideoElement = select "<video id='video' src='' controls/>" >>= addToVideoContainerMuch like jQuery, we can create a new document element by selecting it. Once created, we add it as a child element to the video container.
addToVideoContainer :: JQuery -> Fay JQuery
addToVideoContainer el = videoContainer >>= flip appendTo elGiven an element (el), grab the video container and append the element to it. appendTo takes two parameters where the first one is the parent and the second one is the child. flip turns this around making a new function where the first parameter is the child and the second one is the parent.
Prelude> x a b = a - b
Prelude> y = flip x
Prelude> x 1 2
-1
Prelude> y 1 2
1This allows us to keep the syntax clean using a one-liner. Implicitly, flip appendTo el is being passed the video container like this:
addToVideoContainer el = videoContainer >>= (\ videoContainer' -> flip appendTo el videoContainer')
-- (>>=) :: Fay JQueryA -> (JQueryA -> Fay JQueryB) -> Fay JQueryB
-- (>>=) :: Fay videoContainer -> (videoContainer -> Fay el ) -> Fay elWe could have written this function like the following.
addToVideoContainer :: JQuery -> Fay JQuery
addToVideoContainer el = do
videoContainer' <- videoContainer
appendTo videoContainer' el
-- Or like this:
addToVideoContainer :: JQuery -> Fay JQuery
addToVideoContainer el = videoContainer >>= (\ videoContainer' -> appendTo videoContainer' el)emptyVideoContainer :: Fay JQuery
emptyVideoContainer = videoContainer >>= JQuery.emptyThis clears out the video container document element.
handleVideoFile :: FileReader -> Fay ()
handleVideoFile fr = do
url <- fileReaderResult fr
if "data:video" `isPrefixOf` url
then void $ addVideoElement >>= setAttr "src" url >> setStatusMessage ""
else void $ setStatusMessage "Not a video file."Here is where we check that the data URL has the video type. If it does not, we tell the user that the file is not a video file. However, if we are dealing with a video file, set the video element src to the data URL.
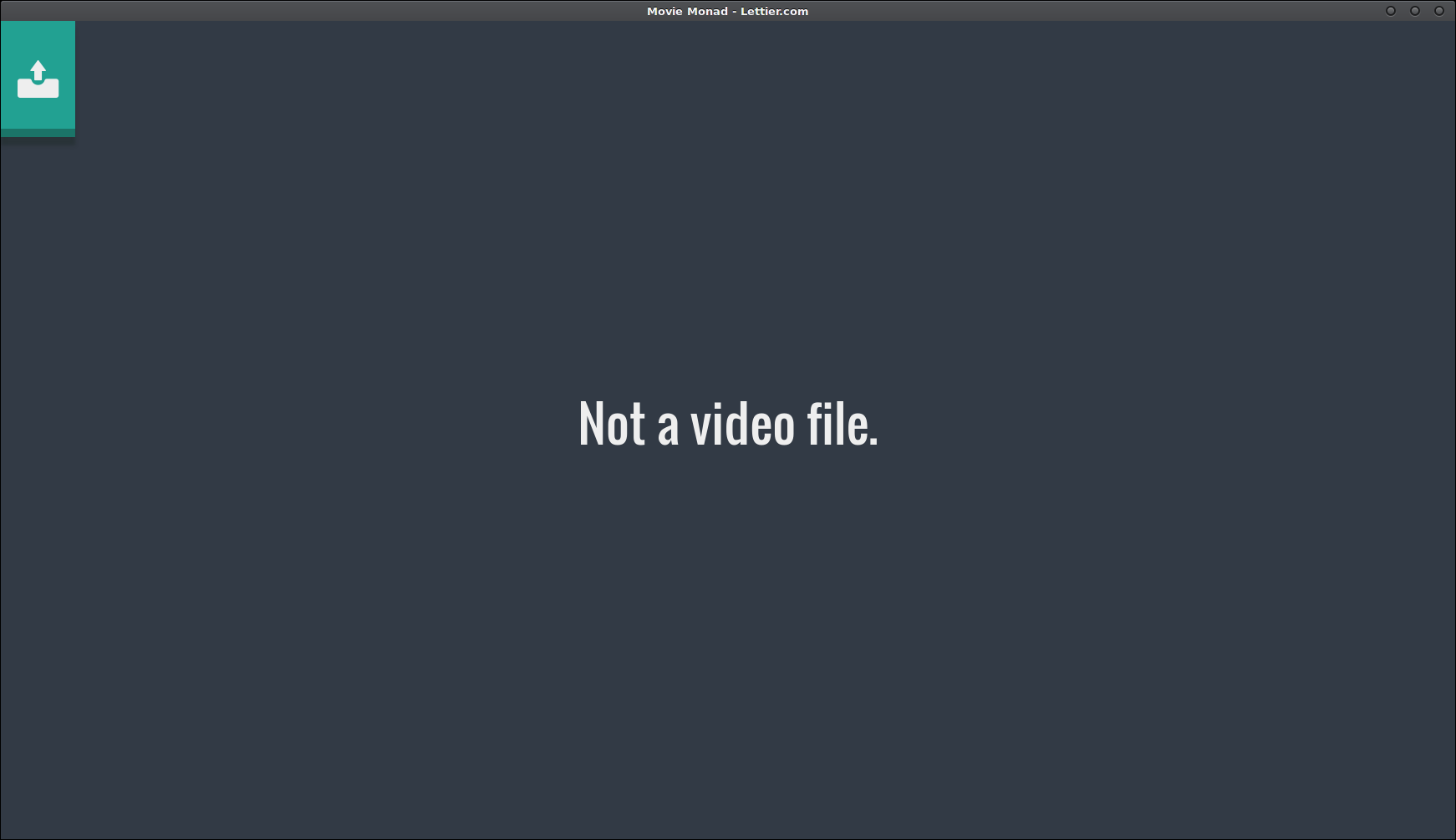
Not a video file.
readAsDataURL :: FileReader -> File -> Fay ()
readAsDataURL = ffi "%1['readAsDataURL'](%2)"At long last we reach the end of the application logic where we read the file in as a data URL such that we can set this URL as the video source.
Below is the entire ~/movieMonad/src/js/Main.hs file–be sure to copy it over.
{-
David Lettier (C) 2016
http://www.lettier.com/
-}
{-# LANGUAGE RebindableSyntax, OverloadedStrings, EmptyDataDecls #-}
import Prelude
import FFI
import JQuery
import Fay.Text
data File
data FileReader
main :: Fay ()
main = startApp
startApp :: Fay ()
startApp = ready $ do
fileInput' <- fileInput
void $ change (const $ onFileInputChange fileInput') fileInput'
fileInput :: Fay JQuery
fileInput = select "#fileInput"
newFileReader :: Fay FileReader
newFileReader = ffi "new FileReader()"
fileInputFiles :: JQuery -> Fay (Nullable [File])
fileInputFiles = ffi "%1['prop']('files')"
fileSize :: File -> Fay Int
fileSize = ffi "%1['size']"
nullableFileSize :: Nullable File -> Fay Int
nullableFileSize nullableFile = case nullableFile of
Nullable file -> fileSize file
Null -> return 0
fileSizeLimit :: Int
fileSizeLimit = 51000000
fileInputFile :: JQuery -> Int -> Fay (Nullable File)
fileInputFile fileInput index = do
nullableFiles <- fileInputFiles fileInput
let files = case nullableFiles of
Nullable files -> files
Null -> []
if Prelude.null files || (Prelude.length files <= index)
then return Null
else return (Nullable $ files!!index)
fileReaderResult :: FileReader -> Fay Text
fileReaderResult = ffi "%1['result']"
addFileReaderEventListener :: FileReader -> Text -> (Event -> Fay ()) -> Fay ()
addFileReaderEventListener = ffi "%1['addEventListener'](%2, %3)"
setUpNewFileRead :: Nullable File -> Fay ()
setUpNewFileRead Null = return ()
setUpNewFileRead (Nullable file) = do
fr <- newFileReader
let onLoadCallback = const $ handleVideoFile fr
addFileReaderEventListener fr "load" onLoadCallback
readAsDataURL fr file
onFileInputChange :: JQuery -> Fay ()
onFileInputChange fileInput = do
emptyVideoContainer
nullableFile <- fileInputFile fileInput 0
nfs <- nullableFileSize nullableFile
if (&&) (nfs > 0) (nfs <= fileSizeLimit)
then setUpNewFileRead nullableFile
else void $ setStatusMessage "File too small or large."
setStatusMessage :: Text -> Fay JQuery
setStatusMessage text = select "#statusMessage" >>= setHtml text
videoContainer :: Fay JQuery
videoContainer = select "#videoContainer"
addVideoElement :: Fay JQuery
addVideoElement = select "<video id='video' src='' controls/>" >>= addToVideoContainer
addToVideoContainer :: JQuery -> Fay JQuery
addToVideoContainer el = videoContainer >>= flip appendTo el
emptyVideoContainer :: Fay JQuery
emptyVideoContainer = videoContainer >>= JQuery.empty
handleVideoFile :: FileReader -> Fay ()
handleVideoFile fr = do
url <- fileReaderResult fr
if "data:video" `isPrefixOf` url
then void $ addVideoElement >>= setAttr "src" url >> setStatusMessage ""
else void $ setStatusMessage "Not a video file."
readAsDataURL :: FileReader -> File -> Fay ()
readAsDataURL = ffi "%1['readAsDataURL'](%2)"Electron Boilerplate
Electron needs/runs a JavaScript file that creates the application window (or windows), defines the window properties, and setups the application callbacks like ready or window-all-close.
{-# LANGUAGE RebindableSyntax, OverloadedStrings, EmptyDataDecls #-}
import Prelude
import FFI
import Fay.TextThe same language extensions and imports as before.
data Electron
data App
data BrowserWindow
data MainWindowNew data types representing the electron, app, browser window, and main window JavaScript objects.
class OnCaller a
instance OnCaller App
instance OnCaller MainWindowHere we create a new type class and declare the data types App and MainWindow members of this type class. On caller means they can call on in the JavaScript world. Now we do not have to write an onEvent function just for App and another one just for MainWindow. The onEvent definition is listed below.
type DirName = TextHere we create a type alias that says DirName is just an alias for the Fay Text type. This provides some clarity in a function type signature. Yes it expects the Text type, but more specifically, it is looking for the result returned by calling __dirname in JavaScript. The DirName is the directory path in which this (eventual) JavaScript file resides.
main :: Fay ()
main = bootApp
bootApp :: Fay ()
bootApp = do
electron' <- electron
app' <- app electron'
onEvent app' "ready" setupMainWindow
onEvent app' "window-all-closed" $ do
processPlatform' <- processPlatform
when (processPlatform' /= "darwin") $ callAppProp app' "quit"
onEvent app' "activate" $ void $ do
nullableMainWindow <- getMainWindow
case nullableMainWindow of
Nullable _ -> return ()
Null -> setupMainWindowHere we gather the electron object and then the app object using the electron object. Two app event listeners are setup where we listen for the window closing and the application activating. If the application window is closed, we call app.quit() in JavaScript. When the activate event fires, we setup the main window if it does not already exist.
electron :: Fay Electron
electron = ffi "require('electron')"require loads the electron module and returns the module object.
processPlatform :: Fay Text
processPlatform = ffi "process.platform"This gives us the platform that Movie Monad is being run on.
app :: Electron -> Fay App
app = ffi "%1['app']"Get the app object from the electron object.
callAppProp :: App -> Text -> Fay ()
callAppProp = ffi "%1[%2]()"This translates to app.someProp();.
browserWindow :: Electron -> Fay BrowserWindow
browserWindow = ffi "%1['BrowserWindow']"Retrieve the BrowserWindow constructor.
dirName :: Fay DirName
dirName = ffi "(function () { return __dirname; })()"Create an IIFE which returns the directory path where this JavaScript file resides. Notice that it returns the DirName type which is aliased to Text.
windowWidth :: Int
windowWidth = 800
windowHeight :: Int
windowHeight = 600The initial window width and height.
windowIcon :: DirName -> Fay Text
windowIcon = ffi "(function (d) { return d + '/icon.png'; })(%1)"This returns the location of the icon file which will eventually show up in the taskbar.
newMainWindow :: BrowserWindow -> Int -> Int -> Text -> Fay MainWindow
newMainWindow = ffi "(function (b) { return global['mainWindow'] = new b({ width: %2, height: %3, icon: %4 }); })(%1)"This is the largest foreign function interface definition we create. As you can see, it creates a new BrowserWindow instance and saves that instance in the global object under the mainWindow property.
Keep a global reference of the window object, if you don’t, the window will be closed automatically when the JavaScript object is garbage collected.
getMainWindow :: Fay (Nullable MainWindow)
getMainWindow = ffi "(function () { var m = global['mainWindow']; return m ? m : null; })()"Look up the main window in the global object. If the object is available, return it, otherwise return null. Because it is possible to return null, we set the return type as Nullable MainWindow.
onEvent :: OnCaller a => a -> Text -> Fay () -> Fay ()
onEvent = ffi "%1['on'](%2, %3)"This can be used with any member of the OnCaller type class. Roughly translated: obj.on('eventType', callbackFunction);.
loadUrl :: MainWindow -> DirName -> Fay ()
loadUrl = ffi "%1['loadURL']('file://' + %2 + '/index.html')"The start of the Movie Monad application begins with the HTML file we created earlier. This will load the user interface into the main application window.
setMainWindowNull :: Fay ()
setMainWindowNull = ffi "(function () { global['mainWindow'] = null; })()"Sets the main window global property to null.
hideMainWindowMenu :: MainWindow -> Fay ()
hideMainWindowMenu = ffi "%1['setMenu'](null)"To simplify the interface, we hide the main menu bar. During development, it is best to leave this visible.
setupMainWindow :: Fay ()
setupMainWindow = do
nullableMainWindow <- getMainWindow
mainWindow <- case nullableMainWindow of
Nullable mainWindow -> return mainWindow
Null -> do
electron' <- electron
browserWindow' <- browserWindow electron'
iconFile <- dirName >>= windowIcon
newMainWindow browserWindow' windowWidth windowHeight iconFile
dirName >>= loadUrl mainWindow
hideMainWindowMenu mainWindow
onEvent mainWindow "close" setMainWindowNullCreates the main window if it does not already exist, hides the menu bar, and sets the main window to null when we receive a close event.
Below is the entire ~/movieMonad/src/ electronBoot/Main.hs file–be sure to copy it over.
{-
David Lettier (C) 2016
http://www.lettier.com/
-}
{-# LANGUAGE RebindableSyntax, OverloadedStrings, EmptyDataDecls #-}
import Prelude
import FFI
import Fay.Text
data Electron
data App
data BrowserWindow
data MainWindow
class OnCaller a
instance OnCaller App
instance OnCaller MainWindow
type DirName = Text
main :: Fay ()
main = bootApp
bootApp :: Fay ()
bootApp = do
electron' <- electron
app' <- app electron'
onEvent app' "ready" setupMainWindow
onEvent app' "window-all-closed" $ do
processPlatform' <- processPlatform
when (processPlatform' /= "darwin") $ callAppProp app' "quit"
onEvent app' "activate" $ void $ do
nullableMainWindow <- getMainWindow
case nullableMainWindow of
Nullable _ -> return ()
Null -> setupMainWindow
electron :: Fay Electron
electron = ffi "require('electron')"
processPlatform :: Fay Text
processPlatform = ffi "process.platform"
app :: Electron -> Fay App
app = ffi "%1['app']"
callAppProp :: App -> Text -> Fay ()
callAppProp = ffi "%1[%2]()"
browserWindow :: Electron -> Fay BrowserWindow
browserWindow = ffi "%1['BrowserWindow']"
dirName :: Fay DirName
dirName = ffi "(function () { return __dirname; })()"
windowWidth :: Int
windowWidth = 800
windowHeight :: Int
windowHeight = 600
windowIcon :: DirName -> Fay Text
windowIcon = ffi "(function (d) { return d + '/icon.png'; })(%1)"
newMainWindow :: BrowserWindow -> Int -> Int -> Text -> Fay MainWindow
newMainWindow = ffi "(function (b) { return global['mainWindow'] = new b({ width: %2, height: %3, icon: %4 }); })(%1)"
getMainWindow :: Fay (Nullable MainWindow)
getMainWindow = ffi "(function () { var m = global['mainWindow']; return m ? m : null; })()"
onEvent :: OnCaller a => a -> Text -> Fay () -> Fay ()
onEvent = ffi "%1['on'](%2, %3)"
loadUrl :: MainWindow -> DirName -> Fay ()
loadUrl = ffi "%1['loadURL']('file://' + %2 + '/index.html')"
setMainWindowNull :: Fay ()
setMainWindowNull = ffi "(function () { global['mainWindow'] = null; })()"
hideMainWindowMenu :: MainWindow -> Fay ()
hideMainWindowMenu = ffi "%1['setMenu'](null)"
setupMainWindow :: Fay ()
setupMainWindow = do
nullableMainWindow <- getMainWindow
mainWindow <- case nullableMainWindow of
Nullable mainWindow -> return mainWindow
Null -> do
electron' <- electron
browserWindow' <- browserWindow electron'
iconFile <- dirName >>= windowIcon
newMainWindow browserWindow' windowWidth windowHeight iconFile
dirName >>= loadUrl mainWindow
hideMainWindowMenu mainWindow
onEvent mainWindow "close" setMainWindowNullBuild
So far we setup our build environment and we wrote out the source code. We are now ready to build the entire project.
cd ~/movieMonad
nvm use
makeIf all went well, you should see the Movie Monad window open and ready to play videos. Located in ~/movieMonad/dist/electronDists are the packaged Linux, Windows, and Mac versions.
~/movieMonad
dist/
electronDists/
movieMonad-darwin-x64/
movieMonad-linux-ia32/
movieMonad-linux-x64/
movieMonad-mas-x64/
movieMonad-win32-ia32/
movieMonad-win32-x64/If later on you only want to do some portion of the build process, you can pass make the target name.
cd ~/movieMonad
nvm use
make buildHaskellEach target or build step is listed in the makefile you created earlier.
Recap
Using the Haskell libraries Blaze, Fay, and Clay, we generated the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files necessary to build Movie Monad. These files, along with Electron and Electron Packager, allowed us to make a video playing desktop application and package it up for distribution to all major platforms. In Let’s make a GTK Video Player with Haskell, we take a different approach and build Movie Monad using GTK+ and GStreamer.
If you enjoy web programming in Haskell, be sure to read Building a Haskell Web API and Haskell to JavaScript.